What is Hip Osteoarthritis and How to Treat it?
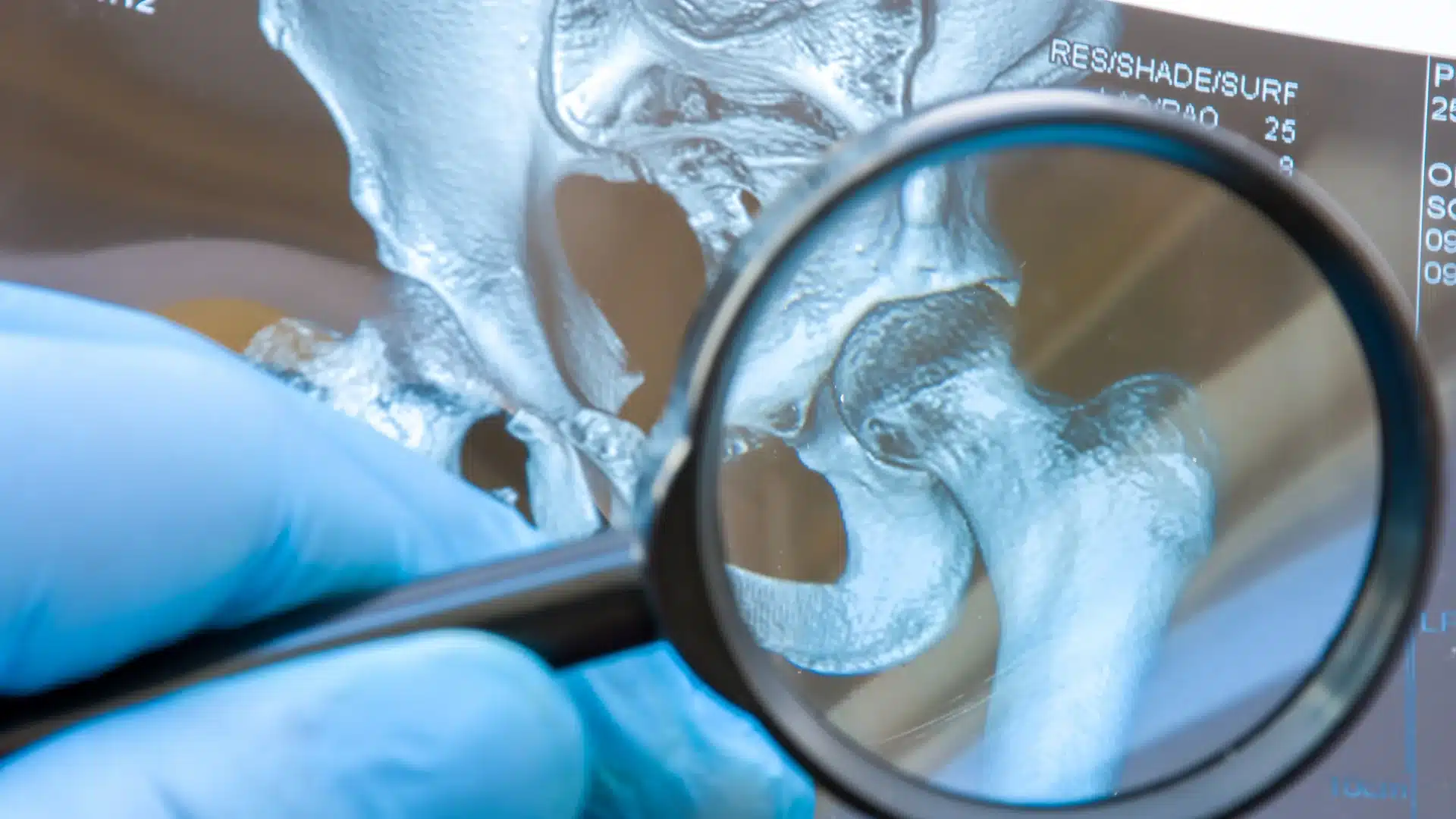
Overview
Hip arthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people in India. It can cause pain, stiffness, and difficulty in everyday activities. If you’re looking for a clear, easy-to-understand explanation of what hip arthritis is and how to manage it, you’re in the right place. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about hip arthritis in simple, relatable terms.
What Is Hip Arthritis?
Arthritis refers to inflammation of the joints, and hip arthritis specifically affects the hip joint. The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint, where the ball-shaped top of the thigh bone fits into the socket of the pelvis. Arthritis in this joint can damage the cartilage, which is a smooth tissue that cushions the bones and helps them move smoothly.
It is the most common type of arthritis and is often called “wear-and-tear” arthritis. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones in the hip joint gradually breaks down over time. As the cartilage wears away, the bones can start to rub directly against each other, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling.
The condition can worsen over time, making daily tasks like walking, climbing stairs, or even sitting uncomfortable. The degeneration of cartilage in OA results in limited mobility, which can affect daily tasks like walking and bending.
Osteoarthritis primarily affects older adults but can also occur in younger people, particularly those with joint injuries or genetic predispositions. Advanced OA may even lead to the development of bone spurs, further restricting movement and causing additional discomfort.
Symptoms
The symptoms of hip arthritis can vary depending on the type and stage of the condition. Let’s look at these in more detail:
1. Pain in the Hip Joint
Pain is one of the most common symptoms of hip arthritis, often felt in the groin, thigh, buttocks, or even the knee. In the early stages, the pain may come and go, typically worsening after physical activity. As the condition progresses, the pain can become constant, even during rest. This persistent pain can interfere with sleep and affect your overall quality of life.
2. Stiffness
Stiffness in the hip joint is another hallmark symptom. It may be most noticeable in the morning or after sitting for a long period. Stiffness can make it difficult to move the hip freely, limiting activities like bending down or getting up from a chair. Over time, the stiffness can worsen, making even simple movements a challenge.
3. Swelling
Inflammation in the joint can cause noticeable swelling around the hip area. Swelling may be accompanied by warmth and tenderness when touched. In autoimmune forms of arthritis like RA, the swelling can be more pronounced and persistent. This inflammation can also lead to the development of nodules or lumps around the joint in some cases.
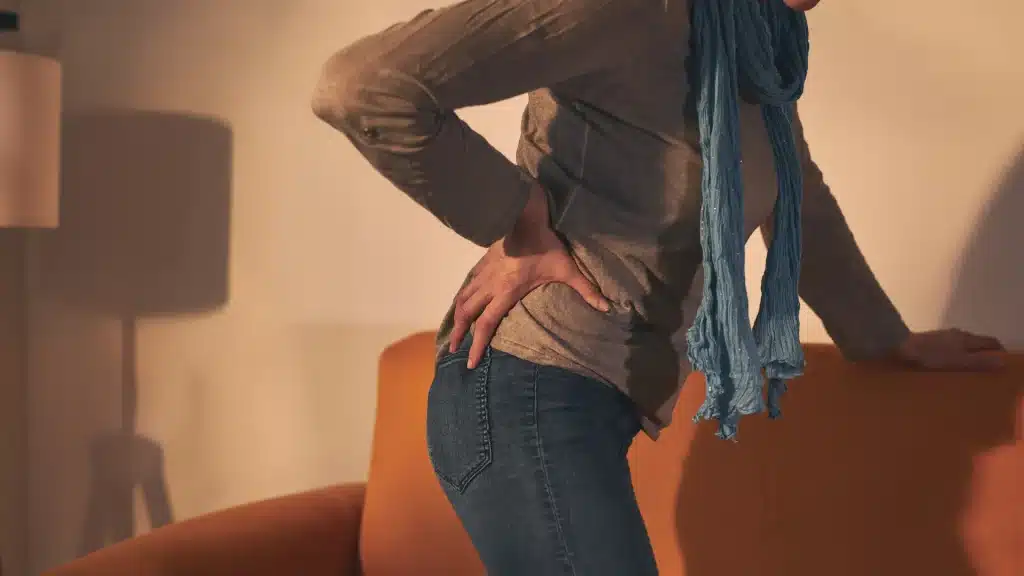

4. Reduced Range of Motion
Hip arthritis can limit the range of motion in the joint, making it difficult to perform simple tasks like putting on shoes or crossing your legs. This is due to the joint becoming less flexible as the cartilage wears away and the bones grow closer together. Reduced range of motion can lead to compensatory movements that may strain other parts of the body, such as the lower back and knees.
5. Grinding or Clicking Sensation
As the cartilage breaks down, you may feel or hear a grinding, clicking, or popping sensation in the hip joint during movement. This is caused by the bones rubbing against each other. This sensation, known as crepitus, can be particularly noticeable during activities that involve bending or twisting motions.
6. Limping
Many people with hip arthritis develop a limp as they try to avoid putting too much weight on the affected joint. This can also lead to imbalance and strain on other parts of the body, such as the lower back and knees. Limping may worsen over time as the joint damage progresses.
Causes and Risk Factors
A variety of factors can cause hip arthritis. Let’s take a closer look:
1. Age
The risk of developing hip arthritis increases with age. The cartilage naturally wears down over time, making elderly individuals more prone to osteoarthritis. Aging also reduces the body’s ability to repair joint damage, leaving the hip more vulnerable to arthritis.
2. Genetics
A family history of arthritis increases your risk. Genetic factors can also influence the severity and progression of arthritis, highlighting the importance of early detection and management.

3. Injury
Past injuries to the hip, such as fractures or dislocations, can increase the likelihood of developing post-traumatic arthritis. Even if the injury heals, it can leave the joint vulnerable to future damage. Athletes and individuals in physically demanding jobs are particularly at risk.
4. Obesity
Carrying excess weight puts extra pressure on the hip joint, accelerating cartilage breakdown. Weight loss is often recommended as a key part of managing arthritis symptoms. Obesity is a significant risk factor for osteoarthritis and can make symptoms worse in all types of hip arthritis.
5. Repetitive Stress
Jobs or activities that involve repetitive motions or heavy lifting can contribute to joint wear and tear. Maintaining proper posture and using ergonomic techniques can reduce the risk. Over time, this stress can lead to the development of arthritis in the hip.
6. Autoimmune Conditions
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis occur when the immune system attacks healthy tissue, leading to chronic inflammation. These conditions are often linked to genetic and environmental triggers. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to managing symptoms and preventing further damage.
Diagnosis
To diagnose hip arthritis, doctors use a combination of methods:
Medical History: Your symptoms and your family history of arthritis forms an important part of the diagnosis.
Physical Exam: A physical exam consisting of checking for pain, swelling, and range of motion in the hip.
Imaging Tests: A number of imaging techniques including X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans can show joint damage, cartilage loss, or inflammation.
Blood Tests: For disorders that can be detected in the blood, for example, it is useful for identifying autoimmune types of arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment
While there’s no cure for hip arthritis, treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are the main options:
1. Lifestyle Changes
Weight Management: Losing weight reduces stress on the hip joint.
Exercise: Low-impact activities like swimming or cycling help strengthen the muscles around the hip.
Physical Therapy: Improves flexibility and range of motion.
2. Medications
Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter options like aspirin or paracetamol can help.
Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Reduce swelling and pain.
Disease-Modifying Drugs (DMARDs): Used for autoimmune arthritis.
Corticosteroid Injections: Provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation.
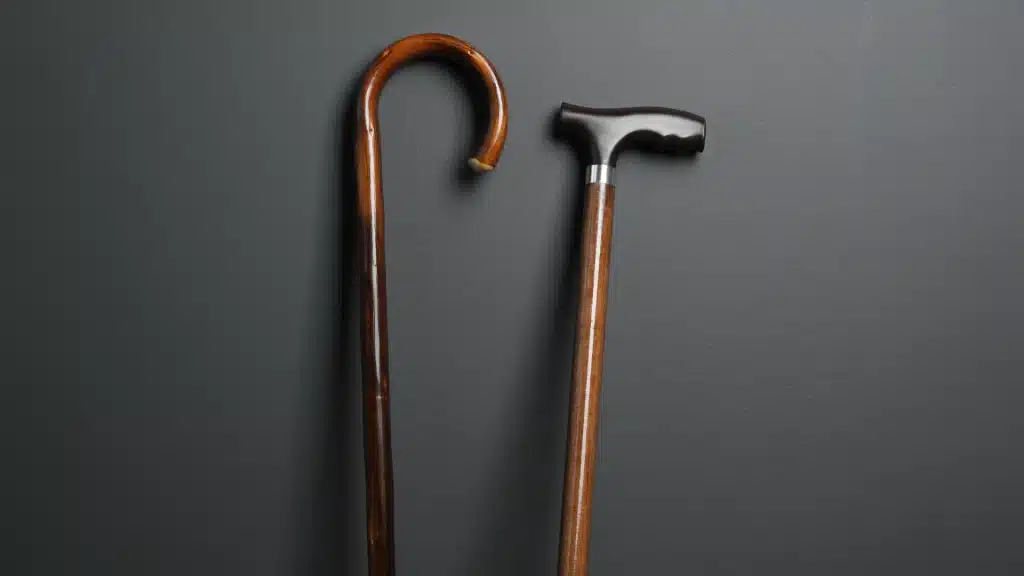

3. Assistive Devices
Canes or Walkers: Help take pressure off the hip joint.
Shoe Inserts: Improve joint alignment and reduce pain.
4. Regenerative Therapy by HipXpert
Be free from hip pain with the help of regenerative cellular therapy that uses your body’s healing potential to treat your hip without surgery.
5. Total Hip Replacement
If your arthritis has completely degraded the hip joint and there is irreversible damage, then total hip arthroplasty or total hip replacement is the only surgical option for treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing when to seek medical advice is crucial for your health and well-being. Consider consulting a healthcare professional if:
1. Interference with Daily Activities
If you are experiencing pain or stiffness that affects your ability to perform everyday tasks such as walking, climbing stairs, or even simple movements like getting dressed, then it is a clear indicator that you should seek medical guidance.
2. Persistent Symptoms
If your symptoms last longer than a few weeks without signs of improvement, it’s essential to get a thorough examination. Continuous symptoms may indicate an underlying condition that requires treatment.
3. Signs of Inflammation
Pay close attention if you notice any swelling, redness, or warmth surrounding a joint. These symptoms could signal infection, inflammation, or injury, which a healthcare provider best assesses to prevent further complications.
4. Ineffective Pain Management
If over-the-counter medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen, are not alleviating your discomfort, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. They can recommend alternative treatments, therapies, or further diagnostic testing as necessary.
Taking these signs seriously can help ensure timely and effective treatment, ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
Takeaways
Hip arthritis is a challenging condition but with the right care and treatment, it’s possible to continue with a normal lifestyle. You can take proactive steps to manage your condition and improve your condition with a treatment suited to your condition. If you’re experiencing hip pain, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider to explore the best treatment plan for you.
FAQs About Hip Arthritis
What is the best exercise for hip arthritis?
Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, and yoga are great for strengthening the hip joint without putting too much stress on it.
How long does a hip replacement last?
A hip replacement is generally designed to last between 15 to 20 years, but many patients experience issues with the artificial hip joint and over the time are unable to follow a prescribed rehabilitation program to take care of their new joint.
Can diet affect hip arthritis?
Yes, diet plays a significant role in managing hip arthritis symptoms. Consuming a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and fatty fish can help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially leading to a decrease in pain and stiffness.
