Avascular Necrosis of Hip: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
Overview
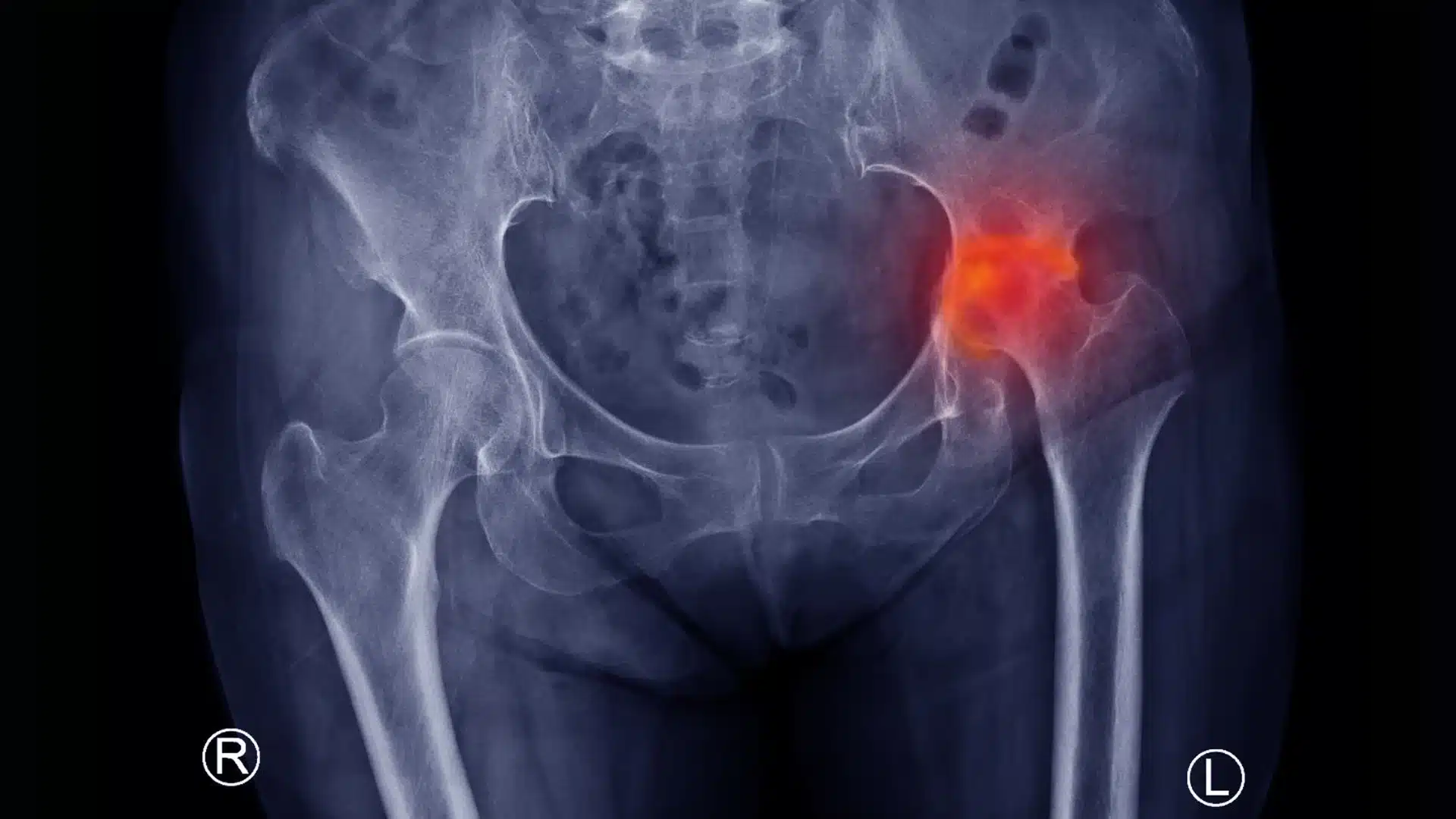
Avascular Necrosis, which is also termed AVN, this problem arises when the flow of blood into the femoral head, which forms the ball portion of the hip joint, is disrupted. The failure of the provision of a blood supply then leads to the death of bone tissue.
Then, there comes hip pain, structural damage, and eventual joint collapse. If not addressed, it can significantly impact the normal functioning of daily activities and further lead to permanent disability. The best precaution is identifying the AVN grade at an early stage and then getting appropriate treatment as well.
What is Osteonecrosis (AVN) of Hip?
Osteonecrosis or Avascular Necrosis can target any of the joints but it is more likely to target your hip joint due to anatomical structure and blood supply of the bones involved in the joint. It can also target the ankles, jaw, knees, upper arms or shoulders.
It can affect anyone but the condition is most common in people of middle age, around 30 to 50 years. You can determine the cause of hip pain using this location diagram.
Causes of AVN Hip
AVN can stem from a variety of factors that compromise blood flow to the hip joint. Some of the most common causes include:
Trauma: Injuries such as hip fractures or dislocations can damage blood vessels, reducing blood supply to the femoral head.
Corticosteroid Use: Long-term or high-dose use of corticosteroid drugs, which are commonly used for inflammatory conditions, may impair bone health and blood circulation.
Alcohol Abuse: Fatty deposits in blood vessels lead to the restriction of blood flow into the bones.
Blood Disorders: Sickle cell anemia or coagulation disorders can lead to poor circulation, thus making a person vulnerable to the development of AVN.
Post COVID-19: An increase in cases of AVN has been seen in people affected by COVID-19 sometime in their lifetime.
Other Medical Conditions: Other chronic diseases can also lead to AVN, such as lupus, kidney disease, or pancreatitis.
Lifestyle Choices: Smoking and non-physical activities are other risk factors that can damage blood circulation.
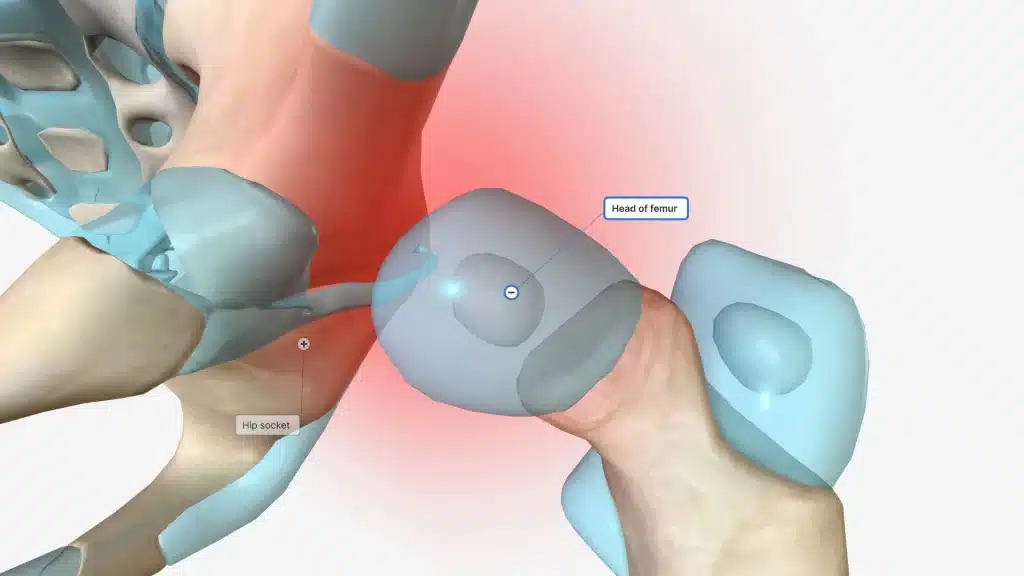
Symptoms of AVN Hip
The symptoms of AVN gradually develop but worsen with the progression of this condition. There can be a wide variety of symptoms seen depending on the individual. Some common indicators include:
Hip Pain: Pain in the groin, thigh, or buttock tends to worsen with exercise.
Limping: Inclination to limp due to pain and instability around the joint. In simple words, walking in the wrong form.
Reduced Range of Motion: Findings that may include challenges performing movements such as bending or rotating the hip.
Stiffness: A feeling of tightness or reduced flexibility in the hip joint.
Loss of Function: In advanced stages, the joint may become severely compromised, limiting daily activities.
Night Pain: For some individuals, pain becomes more noticeable at rest or during sleep.
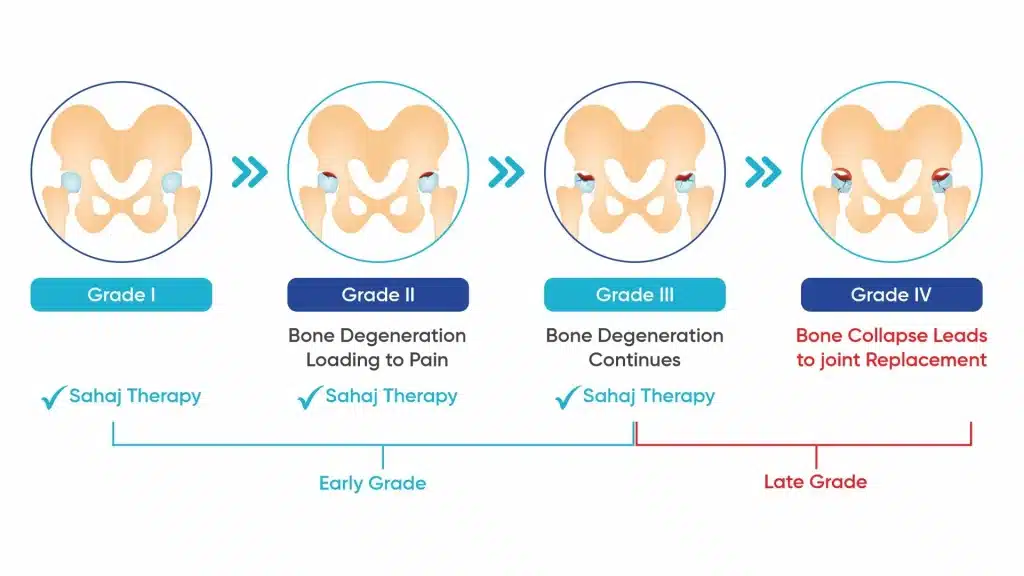
Stages of AVN Hip
Avascular Necrosis of Hip progresses in stages with gradual destruction of the hip joint along with it. The progression of AVN is categorized into four grades:
Grade 1: Early AVN, where blood flow is compromised, but there are no visible changes on X-rays. You will face minimal pain while doing everything.
Grade 2: Mild structural damage is evident on imaging, but the joint remains functional. As the joint remains functional it’s best to get AVN treatment in the first two stages as there are higher chances plus minimal damage in the hip joint.
Grade 3: The femoral head begins to collapse, leading to noticeable deformities and severe pain.
Grade 4: Advanced joint collapse and arthritis develop, severely limiting mobility leading to joint replacement.
Diagnosis and Treatment of AVN Hip
Diagnosis Method
Early diagnosis is crucial in the case of AVN hip pain. Healthcare professionals use a number of ways to ascertain the condition:
X-rays: First imaging to detect the damage in the bone or the shape change of the femoral head
MRI: The most sensitive test for identifying early-stage AVN, revealing changes in bone and soft tissue before they appear on X-rays.
Bone Scan: In bone scan is a scan of your bone to analyze your bones.
CT Scan: Provides detailed images of the joint structure to assess the extent of damage.
Treatment Options
Avascular Necrosis of Hip can be treated by nonsurgical and surgical methods. These are:
Non Surgical Treatment
Medications: In early stages of AVN hip, medications will help to ease the associated symptoms. These include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that help to ease pain, osteoporosis drugs to slow progression, medications that increase blood flow to the bone like Iloprost and some types of blood thinners.
Regenerative Cellular Therapy: You can explore advanced regenerative cellular therapy in the early stages of AVN hip to save your joint. It is a type of autologous grafting (using your cells) done in same surgical sitting using minimal manipulation for your hip joint to regenerate the damaged bone and saving your joint. You can contact us to get a free consultation and find out more.
Electrical Stimulation: Promotes bone healing and regeneration by using electrical currents.
Surgical Treatment
Core Decompression: It involves removing an inner layer of your bone to provide extra space, promote healing by new bone and blood vessels formation, ultimately leading to pain reduction.
Bone Grafting (Transplant): The process of transferring healthy bone tissue from another part of the body to support the damaged area and promote healing.
Hip Joint Replacement: Total hip replacement would be needed in advanced conditions (Grade 4) to facilitate the return of mobility and relief of pain.
Osteotomy: A surgical procedure to remove a part of the bone to relieve stress on the affected weight bearing area and delaying replacement.
Lifestyle Interventions
Getting treatment for AVN is not the only thing. Lifestyle plays a major role in being fit and healthy. In doing that, proper exercise and a nutrient-rich diet are very important in your daily lives to preserve your joint and stay healthy for longer.
Avoid Risk Factors
Risk factors must be minimized to prevent AVN and its progression.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive drinking can impair circulation and bone health.
Avoid Excessive Steroid Use: Work with your healthcare provider to explore alternative treatments if corticosteroids are prescribed.
Protect Your Joints: Use appropriate safety measures during physical activities to avoid traumatic injuries.
Quit Smoking: Smoking reduces blood flow to bones and impairs healing processes.
Mental Well-being: Mental well-being is very important in this modern world.
Living with a chronic condition like AVN is also emotionally difficult. Some coping mechanisms through mindfulness, meditation, or support groups are available for patients to help handle stress.
Takeaways
Avascular necrosis of the hip is a serious condition that needs treatment as early as possible. It is a manageable condition and your goal should be to preserve your hip joint and maintain a healthy life. You can reach out to get a free consultation from HipXpert and get the best treatment regarding your condition.
FAQs About AVN Hip
Is Recovery Possible in AVN Hip Below Grade 3?
Yes, recovery is possible for AVN of the hip below Grade 3. In the early stages (Grade 1 and Grade 2), the bone structure is still intact or only mildly damaged, which allows for more conservative and regenerative treatment options to be effective. Treatments such as regenerative cellular therapy (e.g., AD-SVF), core decompression, medications, and lifestyle modifications can help restore blood flow, promote bone regeneration, and alleviate pain.
Does Hip Replacement Cure Avascular Necrosis?
Hip replacement surgery is a common treatment for advanced stages of Avascular Necrosis (AVN) of the hip, particularly in Grade 4 when there is significant joint collapse and arthritis. Additionally, preserving the natural hip joint through regenerative therapies, especially in the earlier stages of AVN, is often preferable to delay or avoid the need for joint replacement.
Can Exercises Help with Avascular Necrosis of the Hip Joints?
Low-impact exercise can be beneficial for individuals with AVN of the hip, especially in the early stages. It helps maintain joint mobility, strengthen the muscles surrounding the hip, and improve overall cardiovascular health without placing excessive stress on the hip joint. However, in advanced stages of AVN, high-impact activities or exercises that exacerbate hip pain should be avoided to prevent further joint damage.
